
What is the cornea and what role does it play in laser vision correction? |
| 28.03.2019 |
The cornea is the convex outer layer of the front of the eye. The human cornea has a diameter of approximately 11.5 mm, and it is 0,5-0,6 mm thick in the central part and 0,6-0,8 mm in the peripheral part. Behind the cornea, there is the aqueous humour and, further behind, the lens. It is nourished through diffusion – through tears and aqueous humour, as well as neurotrophins provided by the corneal innervation.
The cornea strongly focuses light (about 43 dioptres), better than a lens (about 20 dioptres). However, contrary to the lens, the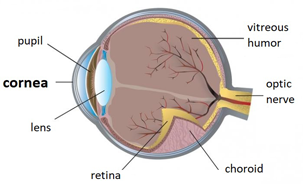 focusing power of the cornea remains stable (is not subject to regulation).
focusing power of the cornea remains stable (is not subject to regulation).
The cornea acts as a shield against dirt, germs and other particles that can damage the eye. It has the same protective function as eyelids, orbital cavities, tears and the sclera (the white of the eye). The cornea also plays an important role in seeing since it helps to focus the light which reaches the eye. This part of the eye is responsible for 65-75% of the total focusing power of the eye.
The cornea and the lens are built in such a way that they can focus the light on the retina, which is light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. When the light reaches the cornea, it bends or refracts the light which reaches the lens. The lens transfers the light onto the retina, which initiates the process of translating the light into images. The retina transforms light into electrical impulses, which are transmitted by the optic nerve to the brain, which interprets them as images.
The refraction process used by the eye resembles the way in which a camera takes a photograph. The cornea and the lens work like the camera lens. The retina can be compared to a photographic film (in older types of cameras) or image sensor (in digital cameras). If the image is not properly focused, the retina creates its blurred version.
The cornea also serves as a filter which helps to eliminate harmful ultraviolet sun radiation. Without this protection, the lens and the retina would be prone to UV radiation-related damage.
In laser vision correction the cornea plays an essential role. Its shape, thickness and steepness have influence on the qualification for the surgery because laser vision correction consists of reshaping the corneal surface.
If you are considering laser vision correction, make an appointment for a qualifying examination, during which the condition of your eyes, including the cornea, will be carefully checked and you will find out whether there are no contraindications to undergoing the procedure.